ESET has collaborated with partners Microsoft, Lumen’s Black Lotus Labs, NTT Ltd. and others in an attempt to disrupt Trickbot botnets. ESET contributed to the project by providing technical analysis, statistical information, and known command and control server domain names and IPs.
Trickbot has infected over a million computing devices around the world since late 2016 and we have been tracking its activities since the beginning. In 2020 alone, our automatic platform analyzed more than 125,000 malicious samples and downloaded and decrypted more than 40,000 configuration files used by the different Trickbot modules, giving us an excellent viewpoint of the different C&C servers used by this botnet.
Trickbot, a long-lasting botnet
Trickbot has been a major nuisance for internet users for a long time. ESET’s first detection for Trickbot was created in late 2016. During these years, Trickbot compromises have been reported in a steady manner, making it one of the largest and longest-lived botnets out there. As reported in our Threat Report Q1 2020, Trickbot is one of the most prevalent banking malware families. As seen in Figure 1, ESET telemetry data shows that this malware strain represents a threat for internet users globally.
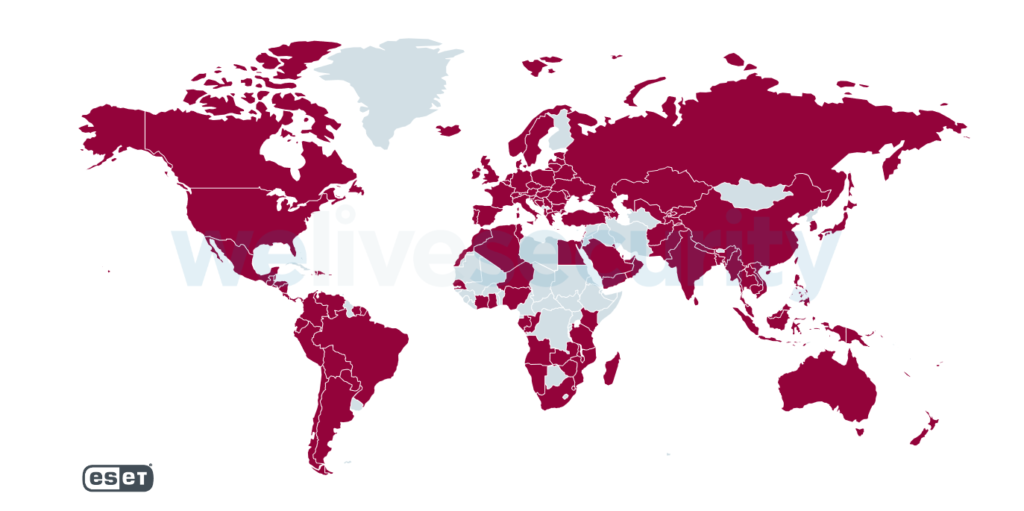
Figure 1. Worldwide Trickbot detections between October 2019 and October 2020
Throughout its existence, Trickbot malware has been distributed in a number of ways. Recently, a chain we observed frequently is Trickbot being dropped on systems already compromised by Emotet, another large botnet. In the past, Trickbot malware was leveraged by its operators mostly as a banking trojan, stealing credentials from online bank accounts and trying to perform fraudulent transfers.
Trickbot’s modular architecture allows it to perform a vast array of malicious actions using a variety of plugins. It can steal all kinds of credentials from a compromised computer and, more recently, has been observed mostly as a delivery mechanism for more damaging attacks, such as ransomware.
One of the oldest plugins developed for the platform allows Trickbot to use web injects, a technique allowing the malware to dynamically change what the user of a compromised system sees when visiting specific websites. To operate, this plugin relies on configuration files downloaded by the main module. These contain information about which websites should be modified and how. Figure 2 shows an excerpt of one such decrypted configuration file containing targeted URLs and the malicious C&C URLs the bot should contact upon the victim accessing the targeted URLs.
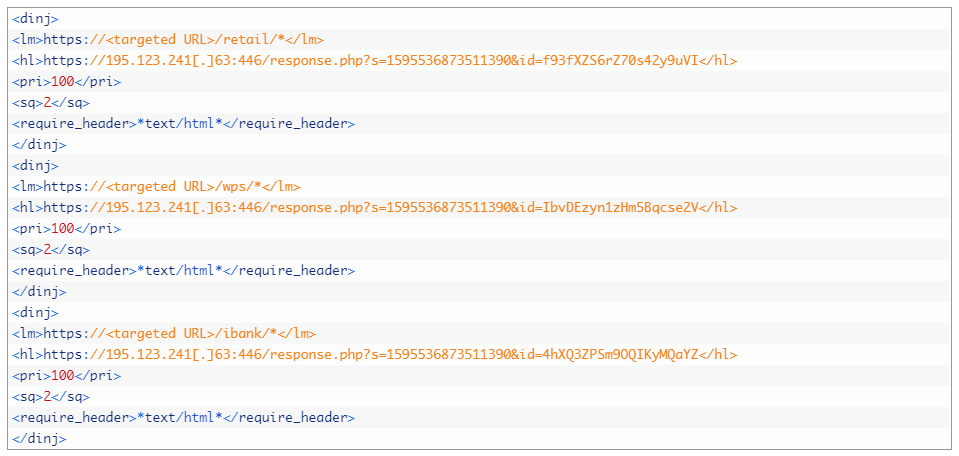
Figure 2. Excerpt of a decrypted dinj configuration file (redacted)
Through our monitoring of Trickbot campaigns, we collected tens of thousands of different configuration files, allowing us to know which websites were targeted by Trickbot’s operators. Figure 3 shows the number of websites extracted from configuration files in 2020.
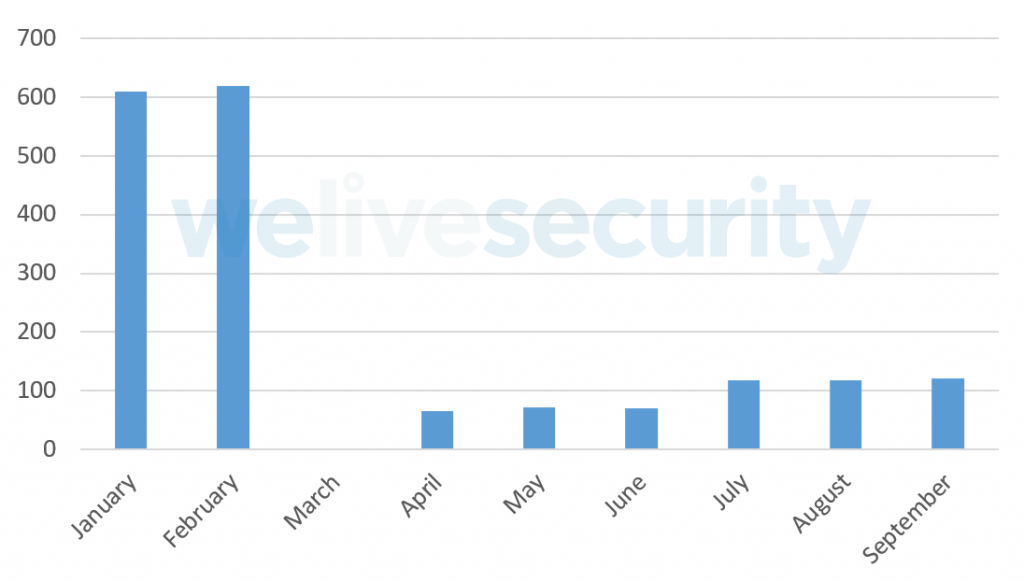
Figure 3. Number of targeted websites in 2020
These targeted URLs mostly belong to financial institutions. There is a sharp drop in the number of targets found in these configuration files starting in March. This coincides with the moment when Trickbot operators dropped the webinject module from the list of default plugins downloaded automatically by the main module — this is why we have no data in March; we had to adjust our processes to maintain visibility on the targeted URLs. This drop in number of targets is likely due to the Trickbot gang starting to focus on another means of monetization during that time frame: ransomware.
In these cases, a Trickbot compromise is first leveraged to perform reconnaissance and lateral movement in an organization’s network and then to drop Ryuk ransomware on as many systems as possible. From the data we have collected, it appears that Trickbot’s operators moved from attempting to steal money from bank accounts, to compromising a whole organization with Trickbot and then using it to execute Ryuk and demand a ransom to unlock the affected systems.
We also observed new malware development projects allegedly coming from Trickbot’s operators, which might also explain their sudden disinterest in operating Trickbot as a banking trojan. One of these projects is the so-called Anchor project, a platform mostly geared towards espionage rather than crimeware. They are also likely involved in the development of the Bazar malware — a loader and backdoor used to deploy malware, such as ransomware, and to steal sensitive data from compromised systems.
Trickbot deep dive
What makes Trickbot so versatile is that its functionalities can be greatly extended with plugins. Throughout our tracking, we were able to collect and analyze 28 different plugins. Some are meant to harvest passwords from browsers, email clients and a variety of applications, while others can modify network traffic or self-propagate. Trickbot plugins are implemented as standard Windows DLLs, usually with at least these four distinctive exports: Start, Control, Release and FreeBuffer.
Interestingly, some have Rich headers while some do not. Rich headers are an undocumented data structure added to all binaries built by Microsoft Visual Studio 97 SP3 or later. They contain information about the development environment where the executable was built. The fact that Rich headers are not always present in plugins — and that when they are present, they show different development environments — leads us to believe that these plugins were written by different developers.
We did not observe many different samples of the different plugins once they were developed and used in the wild. The ones that changed the most are those containing a static configuration file embedded in the binary. These static configuration files contain, among other things, C&C server information, so it is expected to see these change over time. Figure 4 displays the number of variations we saw for each module we collected through our botnet tracker platform. Most of the newer modules’ variants come in pairs: about half of the collected modules were 32-bit versions, while the other half were the 64-bit versions. In the Appendix you can find a brief description of each of these modules.
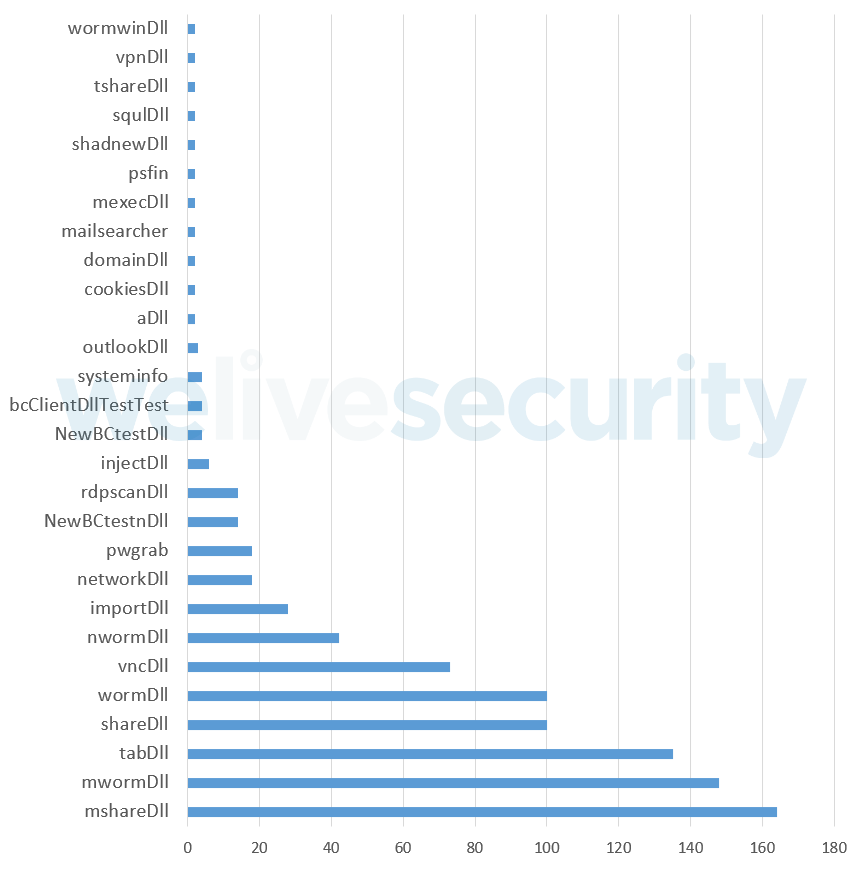
Figure 4. Variant count for each Trickbot plugin
Configuration files for everyone
Although there are potentially many different downloaded configuration files present in a Trickbot installation, the main module contains an encrypted, hardcoded configuration. This contains a list of C&C servers as well as a default list of plugins that should be download.
As mentioned earlier, some plugins also rely on configuration files to operate properly. These plugins rely on the main module to download these configuration files from the C&C servers. Plugins achieve this by passing a small module configuration structure, stored in the plugin binary’s overlay section, that lets the main module know what it should download.
Being able to gather these configuration files allowed us to map the network infrastructure of Trickbot. The main module uses its list of hardcoded C&C servers and connects to one of them to download a second list of C&C servers, the so-called psrv list. The main module contacts this second layer of C&C servers to download the default plugins specified in the hardcoded configuration file. Other modules can be downloaded later upon receiving a command to do so from the Trickbot operators. Some of the plugins, such as the injectDll plugin, for example, have their own C&C servers, which contain configuration files. Finally, there are dedicated C&C servers for plugins. The most prevalent of them are so-called dpost servers, used to exfiltrate stolen data such as credentials but, as detailed in the Appendix, others exist. All these different layers make the disruption effort more challenging. Figure 5 illustrates this initial communication process.
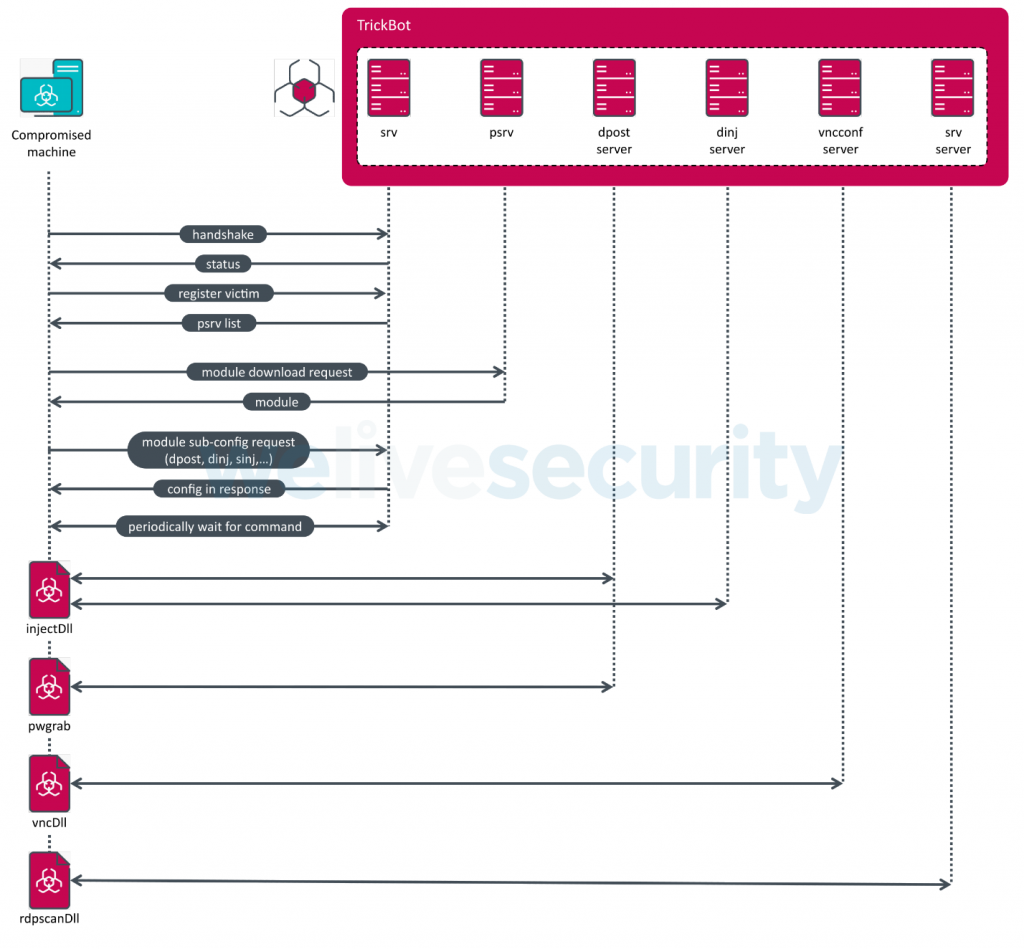
Figure 5. Trickbot network communication process
We have been tracking these different C&C servers since early 2017. This knowledge was, of course, vital in the disruption effort, since we were able to contribute to mapping the network infrastructure used by the malicious actors.
Another interesting artifact we were able to gather through crawling this botnet is the unique identifier present in each Trickbot sample, the so-called gtag. This a string present in the initial hardcoded configuration file identifying different Trickbot campaigns or mode of compromise. For example, the mor campaigns are believed to be Trickbot compromises due to Emotet. gtags can also sometimes indicate the target of a campaign. A good example is uk03-1, which predominantly targeted financial institutions in the United Kingdom.
Figure 6 presents a timeline of all gtags we extracted from Trickbot configuration files from September 2019 to September 2020. Looking at the mor group, we can see the abrupt stop of the Emotet campaigns in April 2020. There are also some groups that are used by specific modules. The tot, jim and lib groups are some of the most continuously seen gtags and are associated with the mshare, nworm/mworm and tab modules respectively, according to a recent Unit42 blogpost. As all of these are used for lateral movement, it is not surprising to see a mostly constant line in their timeline.
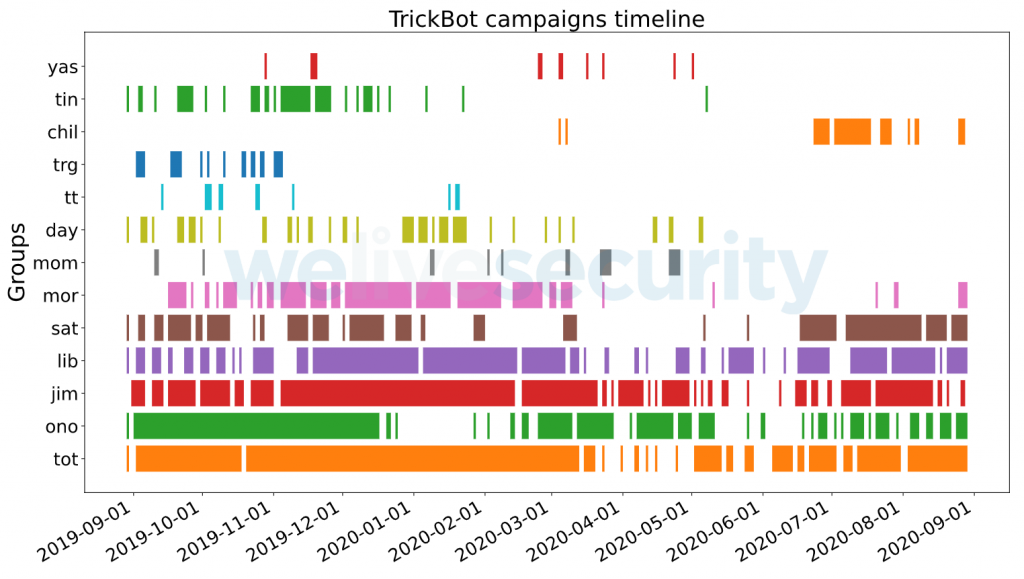
Figure 6. gtags group timeline
Closing remarks
Trying to disrupt an elusive threat such as Trickbot is very challenging and complex. It has various fallback mechanisms and its interconnection with other highly active cybercriminal actors in the underground makes the overall operation extremely complex. We will continue to track this threat and assess the impact that such actions can have on such a sprawling botnet in the long run.
Special thanks to Jakub Tomanek, Jozef Dúc, Zoltán Rusnák and Filip Mazán
ESET detection names
Win32/TrickBot
Win64/TrickBot
MITRE ATT&CK techniques
Note: This table was built using version 7 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
| Tactic | ID | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Access | T1566.001 | Phishing: Spearphishing Attachment | Trickbot has used an email with an Excel sheet containing a malicious macro to deploy the malware. |
| Execution | T1059.003 | Command and Scripting Interpreter: Windows Command Shell | Trickbot has used cmd.exe /c to download and deploy the malware on the user’s machine. |
| T1059.005 | Command and Scripting Interpreter: Visual Basic | Trickbot has used macros in Excel documents to download and deploy the malware on the user’s machine. | |
| T1106 | Native API | Trickbot uses the Windows API CreateProcessW to manage execution flow. | |
| T1204.002 | User Execution: Malicious File | Trickbot has attempted to get users to launch a malicious Excel attachment to deliver its payload. | |
| T1059.007 | Command and Scripting Interpreter: JavaScript/Jscript | Trickbot group used obfuscated JavaScript to download Trickbot loader. | |
| T1559.001 | Inter-Process Communication: Component Object Model | Trickbot used COM to setup scheduled task for persistence. | |
| Persistence | T1547.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder | Trickbot establishes persistence in the Startup folder. |
| T1053.005 | Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task | Trickbot creates a scheduled task on the system that provides persistence. | |
| Privilege Escalation | T1055.012 | Process Injection: Process Hollowing | Trickbot injects into the svchost.exe process. |
| Defense Evasion | T1140 | Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information | Trickbot decodes its configuration data and modules. |
| T1562.001 | Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Tools | Trickbot can disable Windows Defender. | |
| T1112 | Modify Registry | Trickbot can modify registry entries. | |
| T1027 | Obfuscated Files or Information | Trickbot uses non-descriptive names to hide functionality and uses an AES-CBC (256 bits) encryption algorithm for its loader and configuration files. | |
| T1027.002 | Software Packing | Trickbot leverages a custom packer to obfuscate its functionality. | |
| T1553 | Subvert Trust Controls | Trickbot uses signed loaders with stolen valid certificates. | |
| Credential Access | T1555.003 | Credentials from Password Stores: Credentials from Web Browsers | Trickbot can obtain passwords stored by web browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Edge. |
| T1056.004 | Input Capture: Credential API Hooking | Trickbot has the ability to capture RDP credentials by capturing the CredEnumerateA API. | |
| T1552.001 | Unsecured Credentials: Credentials In Files | Trickbot can obtain passwords stored by several applications such as Outlook, Filezilla, and WinSCP. Additionally, it searches for the .vnc.lnk suffix to steal VNC credentials. | |
| T1552.002 | Unsecured Credentials: Credentials in Registry | Trickbot can retrieve PuTTY credentials from the Software\SimonTatham\Putty\Sessions registry key. | |
| T1110 | Brute Force | Trickbot uses brute-force attack against RDP with rdpscanDll module. | |
| Discovery | T1087.001 | Account Discovery: Local Account | Trickbot collects the users of the system. |
| T1087.003 | Account Discovery: Email Account | Trickbot collects email addresses from Outlook. | |
| T1082 | System Information Discovery | Trickbot gathers the OS version, CPU type, amount of RAM available from the victim’s machine. | |
| T1083 | File and Directory Discovery | Trickbot searches the system for all of the following file extensions: .avi, .mov, .mkv, .mpeg, .mpeg4, .mp4, .mp3, .wav, .ogg, .jpeg, .jpg, .png, .bmp, .gif, .tiff, .ico, .xlsx, and .zip. It can also obtain browsing history, cookies, and plugin information. | |
| T1016 | System Network Configuration Discovery | Trickbot obtains the IP address and other relevant network information from the victim’s machine. | |
| T1007 | System Service Discovery | Trickbot collects a list of installed programs and services on the system’s machine. | |
| T1135 | Network Share Discovery | Trickbot module shareDll/mshareDll discovers network shares via the WNetOpenEnumA API. | |
| T1057 | Process Discovery | Trickbot uses module networkDll for process list discovery. | |
| Lateral Movement | T1210 | Exploitation of Remote Services | Trickbot utilizes EthernalBlue and EthernalRomance exploits for lateral movement in the modules wormwinDll, wormDll, mwormDll, nwormDll, tabDll. |
| Collection | T1005 | Data from Local System | Trickbot collects local files and information from the victim’s local machine. |
| T1185 | Man in the Browser | Trickbot uses web injects and browser redirection to trick victims into providing their login credentials on a fake or modified web page. | |
| Command and Control | T1071.001 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | Trickbot uses HTTPS to communicate with its C&C servers, to get malware updates, modules that perform most of the malware logic and various configuration files. |
| T1573.001 | Encrypted Channel: Symmetric Cryptography | Trickbot uses a custom crypter leveraging Microsoft’s CryptoAPI to encrypt C&C traffic. | |
| T1105 | Ingress Tool Transfer | Trickbot downloads several additional files and saves them to the victim’s machine. | |
| T1571 | Non-Standard Port | Some Trickbot samples have used HTTP over ports 447 and 8082 for C&C. | |
| T1219 | Remote Access Software | Trickbot uses vncDll module to remote control the victim machine. | |
| Exfiltration | T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | Trickbot exfiltrates data over the C&C channel using HTTP POST requests. |
Appendix
Lateral movement modules
- shareDll, mshareDll, tshareDll
- Modules used to propagate Trickbot loader to connected network shares of the victimized machine.
- wormwinDll, wormDll, mwormDll, nwormDll
- Modules used for spreading inside a local network of infected machines via SMB. It uses the EternalBlue exploit.
- tabDll
- Module used to spread into the network using the EternalRomance exploit.
Infostealers
- pwgrab
- Password stealer module.
- systeminfo
- Module used for gathering information about the victim machine.
- domainDll
- Module used for stealing credentials and other data from the Domain Controller via LDAP.
- networkDll
- Module used to collect system information and network topology.
- outlookDll
- Module used for stealing credentials from Microsoft Outlook.
- importDll
- Module used for stealing browser information such as cookies, browser history, configurations.
- mailsearcher
- Module used to search for files on the victim machine against a list of hardcoded extensions (documents, images, video).
- cookiesDll
- Web browser cookie stealer module.
- squlDll
- Module used to harvest email addresses from the SQL server and scrape credentials from the infected system with the Mimikatz utility.
- aDll
- Steals Active Directory database.
- psfin
- Module queries the Active Directory for specific string constants which are related to Point-of-Sale software.
Network abuse
- injectDll
- Webinject module.
- NewBCtestDll, NewBCtestnDll
- Module that is a reverse proxy and is able to execute commands.
- vncDll
- Module used as a RAT on the victim machine.
- vpnDll
- Module used to create VPN proxy routed to a given address.
- rdpscanDll
- Module used for brute forcing RDP on a certain list of targets.
- bcClientDllTestTest
- An old module used to proxy Trickbot operator traffic through a victim machine.
- shadnewDll
- Man-in-the-Browser module. It contains a full implementation of IcedID main module. It can intercept web traffic on the victim machine.
Other
- mexecDll
- General purpose “download and execute” module.
| Module names | Sub-config | Rich headers |
|---|---|---|
| shareDll, mshareDll, tshareDll | NO | |
| wormwinDll, wormDll, mwormDll, nwormDll | NO | |
| tabDll | dpost | YES |
| pwgrab | dpost | YES |
| systeminfo | YES | |
| domainDll | NO | |
| networkDll | dpost | YES |
| outlookDll | NO | |
| importDll | NO | |
| mailsearcher | mailconf | NO |
| cookiesDll | dpost | YES |
| squlDll | YES | |
| aDll | YES | |
| psfin | dpost | YES |
| injectDll | dinj, sinj, dpost | YES/NO |
| NewBCtestDll, NewBCtestnDll | bcconfig3 | YES |
| vncDll | vncconf | YES |
| vpnDll | vpnsrv | YES |
| rdpscanDll | srv | YES |
| bcClientDllTestTest | YES | |
| shadnewDll | dom | YES |
| mexecDll | YES |
Useful links:
Microsoft blog post: https://blogs.microsoft.com/on-the-issues/?p=64132
Source: Welivesecurity





Share Article